Recently I have been working on some integration projects which require custom APIs to be built in Magento. As we know Magento support SOAP and REST as 2 main types of APIs. SOAP used to be the main API suite in Magento 1. But REST has become the main stream web API that developers are building nowadays. Magento 2 still support SOAP but I think more people will use REST. Here I want to show you how to build REST APIs in Magento 2(M2).
One of the main features of M2 is that it has a much much better support for building custom APIs. By utilising the service contract(a.k.a. PHP interfaces), M2 allows new custom APIs to be added to the suite quickly in a manageable manner. According to the doc, we as developers do not have to handle authentication in our code, this has been taken care of by Magento framework so the idea is to focus on the business logic in the API we are going to built.
So we are going to build a custom API which searches the customer by email in a simple GET request. Although there is a search API, it is a bit of too much effort to build the long URL for such a simple request.
Create a demo module
We will create a demo module Myan/ApiDemo under app/code
Create the module.xml file under MODULE_DIR/etc
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| <?xml version="1.0"?> | |
| <config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" | |
| xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:Module/etc/module.xsd"> | |
| <module name="Myan_ApiDemo" setup_version="1.0.0"/> | |
| </config> |
Create the registration.php file under the module root directory
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| <?php | |
| \Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar::register( | |
| \Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar::MODULE, | |
| 'Myan_ApiDemo', | |
| __DIR__ | |
| ); |
Define the API
This is to use the so called ‘Service Contract’ to define the API including what URL, what request method, what request parameters and response will look like for this API. It is done by both xml configuration file and PHP interfaces.
Create the webapi.xml under the etc directory under the module directory
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| <?xml version="1.0"?> | |
| <routes xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:module:Magento_Webapi:etc/webapi.xsd"> | |
| <route url="/V1/customers/:email" method="GET"> | |
| <service class="Myan\ApiDemo\Api\CustomerManagementInterface" method="getCustomerByEmail"/> | |
| <resources> | |
| <resource ref="Myan_ApiDemo::ApiDemo" /> | |
| </resources> | |
| </route> | |
| </routes> |
The above xml is pretty straight forward and easy to understand. The parameter :email is the dynamic placeholder of the request parameter. Since we only allow authenticated API client to be able to use this API. We set the resource so only clients that have permission to access this resource Myan_ApiDemo::customer can access this API. This is handled by Magento so we do not need to worry about this.
Define the acl.xml for the resource.
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| <?xml version="1.0"?> | |
| <config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:Acl/etc/acl.xsd"> | |
| <acl> | |
| <resources> | |
| <resource id="Magento_Backend::admin"> | |
| <resource id="Myan_ApiDemo::ApiDemo" title="ApiDemo" translate="title" sortOrder="100" /> | |
| </resource> | |
| </resources> | |
| </acl> | |
| </config> |
So this is the new resource showing in the Magento admin

Define the service interface
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| <?php | |
| /** | |
| * Created by PhpStorm. | |
| * User: mingyan | |
| * Date: 11/8/18 | |
| * Time: 9:09 PM | |
| */ | |
| namespace Myan\ApiDemo\Api; | |
| /** | |
| * Interface CustomerManagementInterface | |
| * @package Myan\ApiDemo\Api | |
| * @api | |
| */ | |
| interface CustomerManagementInterface | |
| { | |
| /** | |
| * @param string $email | |
| * @return \Myan\ApiDemo\Api\Data\CustomerInterface | |
| */ | |
| public function getCustomerByEmail($email); | |
| } |
Pay attention to the DocBlock annotations. Magento reads the annotations to understand the request param and response data type when it parses request params and renders the response. All API interfaces need to have @api annotation.
In the response, for demo purposes, we return a customer JSON object with these fields, first_name, last_name, email, dob and magento_id. To return non scalar value, we need to define the object structure in another interface, so called ‘Data Interface’, so that Magento is able to recognise and parse the response properly. I didn’t do it the first time, just returned an array with json_encode. Magento gave me fatal errors complaining about the unrecognised data object. So here is the data interface,
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| <?php | |
| /** | |
| * Created by PhpStorm. | |
| * User: mingyan | |
| * Date: 11/8/18 | |
| * Time: 9:14 PM | |
| */ | |
| namespace Myan\ApiDemo\Api\Data; | |
| use Magento\Framework\Api\ExtensibleDataInterface; | |
| /** | |
| * Interface Customer | |
| * @package Myan\ApiDemo\Api\Data | |
| * @api | |
| */ | |
| interface CustomerInterface extends ExtensibleDataInterface | |
| { | |
| /** | |
| * Constants defined for keys of the data array. | |
| */ | |
| const FIRST_NAME = 'firstName'; | |
| const LAST_NAME = 'lastName'; | |
| const EMAIL = 'email'; | |
| const DOB = 'dob'; | |
| const MAGENTO_ID = 'magentoId'; | |
| /** | |
| * @return string|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getFirstName(); | |
| /** | |
| * @return string|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getLastName(); | |
| /** | |
| * @return string|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getEmail(); | |
| /** | |
| * @return string|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getDob(); | |
| /** | |
| * @return string|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getMagentoId(); | |
| /** | |
| * @param $firstName | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setFirstName($firstName); | |
| /** | |
| * @param $lastName | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setLastName($lastName); | |
| /** | |
| * @param $email | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setEmail($email); | |
| /** | |
| * @param $dob | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setDob($dob); | |
| /** | |
| * @param $magentoId | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setMagentoId($magentoId); | |
| } |
There are getters and setters which will be used for Magento to access the data when it renders the response and parses the request.
Implement the interfaces to implement the API
We can now create concrete classes to implement the interfaces (a.k.a Service Contract in Magento2) to handle the request and return the result. Since Magento framework handles the request parsing, authentication and response rendering, we can focus on our custom API and return the result. With the above configuration, Magento will render the result in proper JSON automatically.
Create a model that implements CustomerManagementInterface.
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| <?php | |
| /** | |
| * Created by PhpStorm. | |
| * User: mingyan | |
| * Date: 11/8/18 | |
| * Time: 10:13 PM | |
| */ | |
| namespace Myan\ApiDemo\Model; | |
| use Magento\Customer\Model\ResourceModel\CustomerRepository; | |
| use Myan\ApiDemo\Model\Data\Customer; | |
| class CustomerManagement implements \Myan\ApiDemo\Api\CustomerManagementInterface | |
| { | |
| protected $customerRepository; | |
| public function __construct( | |
| CustomerRepository $customerRepository | |
| ) | |
| { | |
| $this->customerRepository = $customerRepository; | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @param string $email | |
| * @return \Myan\ApiDemo\Api\Data\CustomerInterface | |
| */ | |
| public function getCustomerByEmail($email) | |
| { | |
| $customer = new Customer(); | |
| //Get customer by email in Magento | |
| $mageCustomer = $this->customerRepository->get($email, null); | |
| $customer->setFirstName($mageCustomer->getFirstname()); | |
| $customer->setLastName($mageCustomer->getLastname()); | |
| $customer->setEmail($mageCustomer->getEmail()); | |
| $dob = $mageCustomer->getDob(); | |
| if (!empty($dob)) { | |
| $customer->setDob($dob); | |
| } | |
| $customer->setMagentoId($mageCustomer->getId()); | |
| return $customer; | |
| } | |
| } |
Because CustomerRepository throws out exception when no customer is found and this exception is translated by Magento as a 404 response back, we do not need to handle not found case in our code.
Create a Customer model to store the data.
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| <?php | |
| /** | |
| * Created by PhpStorm. | |
| * User: mingyan | |
| * Date: 11/8/18 | |
| * Time: 10:15 PM | |
| */ | |
| namespace Myan\ApiDemo\Model\Data; | |
| use Magento\Framework\Api\AbstractSimpleObject; | |
| use Myan\ApiDemo\Api\Data\CustomerInterface; | |
| class Customer extends AbstractSimpleObject implements CustomerInterface | |
| { | |
| /** | |
| * @return string|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getFirstName() | |
| { | |
| return $this->_get(self::FIRST_NAME); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @return string|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getLastName() | |
| { | |
| return $this->_get(self::LAST_NAME); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @return string|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getEmail() | |
| { | |
| return $this->_get(self::EMAIL); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @return string|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getDob() | |
| { | |
| return $this->_get(self::DOB); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @return int|null | |
| */ | |
| public function getMagentoId() | |
| { | |
| return $this->_get(self::MAGENTO_ID); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @param $firstName | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setFirstName($firstName) | |
| { | |
| return $this->setData(self::FIRST_NAME, $firstName); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @param $lastName | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setLastName($lastName) | |
| { | |
| return $this->setData(self::LAST_NAME, $lastName); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @param $email | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setEmail($email) | |
| { | |
| return $this->setData(self::EMAIL, $email); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @param $dob | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setDob($dob) | |
| { | |
| return $this->setData(self::DOB, $dob); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * @param $magentoId | |
| * @return $this | |
| */ | |
| public function setMagentoId($magentoId) | |
| { | |
| return $this->setData(self::MAGENTO_ID, $magentoId); | |
| } | |
| } |
The last step is to configure di.xml to specify the concrete classes for the interfaces for Magento ObjectManager to instantiate the right classes properly.
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| <?xml version="1.0"?> | |
| <config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:ObjectManager/etc/config.xsd"> | |
| <preference for="Myan\ApiDemo\Api\CustomerManagementInterface" | |
| type="Myan\ApiDemo\Model\CustomerManagement" /> | |
| <preference for="Myan\ApiDemo\Api\Data\CustomerInterface" | |
| type="Myan\ApiDemo\Model\Data\Customer" /> | |
| </config> |
That should be it.
Trying out the API
Flush the Magento cache and try to hit the new API URL: https://magento22.test/rest/default/V1/customers/my@test.com in our case. We got this response.

That means our API endpoint has been picked up by Magento and the authentication works because we didn’t send the access token in the header. By the way, there are a few authentication methods that Magento supports, see here for detail. For the simplicity, I will use token base authentication which requires an access token in the header.
For token based authentication, we can use the admin login to get the access token which expires every 4 hours. We can also create an integration in the admin. This also generates a set of token and secret keys which never expires. See Magento doc for detail. Here I create a new integration, 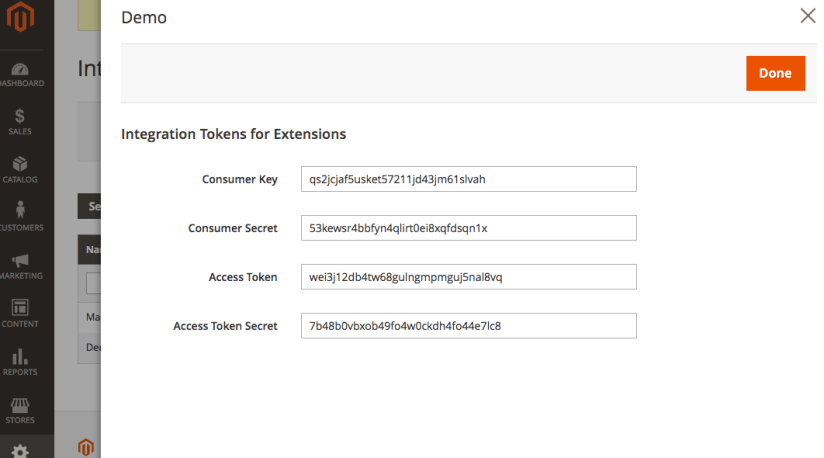
Make sure the integration is given permission to access resource ApiDemo. We only need to pass in the Access Token in the request header
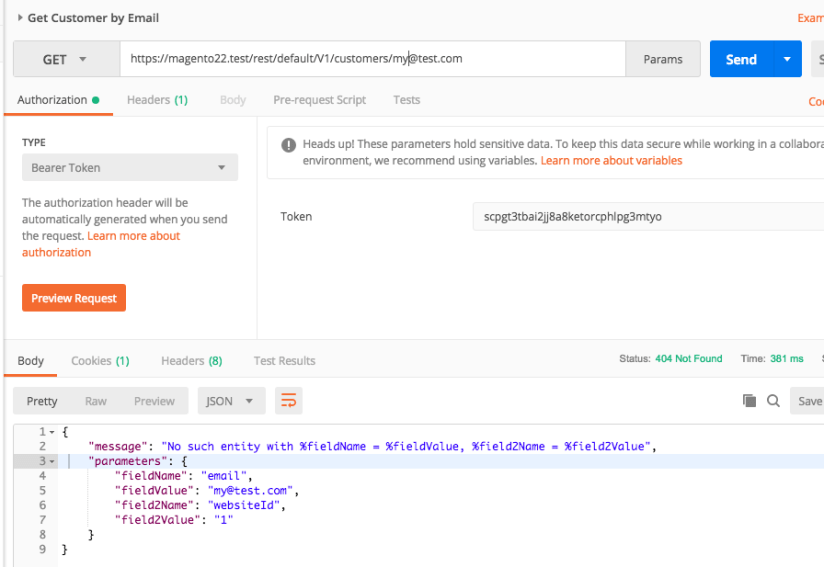
This time we have 404 error rather than 401. So the authentication is ok but there is no such customer under this email. This error was generated by Magento based on the exception thrown from the CustomerRepository.
Now lets try the sample customer email that comes with the Magento Sample Data Module. Bingle! We have 200 response with the customer object formatted in JSON as below. Notice that the keys have been converted from camel case to snake case which is done by Magento as well.

Thoughts
In Magento2, it does make it easier to create custom APIs. Magento 2 takes care of the heavy lifting job for parsing the request, authentication, authorisation and response rendering for us so that is pretty good. However, you have to follow the Magento’s way to write your API otherwise it will give you some hard time. I think that makes sense for Magento to standardise the API creation so it is more consistent and manageable.
But sometimes I also feel that this comes at the cost of heavy configuration as well as quite a few boilerplate code when you want to pass or return JSON objects or JSON arrays. There are some REST request methods not supported by Magento out of the box so you can not do HEAD, PATCH requests unless you override the core functions. These request methods are sometimes useful. Like you can do HEAD to check if the email is available for new customers.
Anyway, I think Magento 2 has much better support for writing APIs compared to M1. And that is good! By the way, you can find the full source code in my Github repository here. Thanks.
